Introduction
The aim of this guide is to enable personnel to develop both competent and confident to carry out suitable assessments in relation to Display Screen Equipment. Including DSE workstations in order to ensure that they comply with the relevant regulations.
What is Display Screen Equipment?
Display Screen Equipment (DSE) includes desktop computers, laptop computers, tablets and workstations where there are monitors and keyboards.
This includes displays on machinery and process equipment, such as checkout desks and programmable systems.
Why do we need training on the safe use of DSE?
The use of DSE or VDU (Visual Display Units) is associated with health problems such as…
- Back ache
- Fatigue
- Stress
- Temporary eye strain
- Headaches
- Upper limb disorders, such as pains in the…
- neck
- arms
- elbows
- wrists
- hands
- fingers
Legal duties
Health and safety legislation relating specifically to DSE requires that…
Risks to individual users at their workstations must be assessed. Measures are taken to reduce the risk of injury or ill health.
The law requires that workstations should meet specified minimum standards and the work activities should be planned so that operatives are allocated breaks from the workstation, usually resulting in changes of activity.
The law also requires that eye tests are provided for DSE users and, where necessary, basic glasses to correct vision problems are provided by the employer.
Employers duties...
Along with other legislation, Employers also have duties under PUWER (the Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations), such as…
- All equipment must be suitably maintained and safe to use
- Information, instruction and training must be provided to employees
- Adequate provision of heating, lighting and ventilation in workplaces
What is a DSE user?

Due to a combination of factors and risks it is impossible to lay down hard-and-fast rules (e.g. based on set hours’ usage per day or week) about who should be classified as a user.
However, it will generally be appropriate to classify employees as users under the DSE Regulations if they:
- Normally use DSE (including mobile devices) for continuous spells of an hour or more at a time.
- Near-continuous spells of an hour or more at a time.
- Use DSE in this way daily.
- Have to transfer information quickly to or from the DSE.
- Need to apply high levels of attention and concentration.
- Are highly dependent on DSE or have little choice about using it.
Regardless - Risk Assess
Regardless of whether or not staff are classed as “users” under the DSE Regulations, Health and Safety Regulations require employers to carry out a risk assessment and reduce any identified risks. This applies to mobile device use and mobile working.
Health effects
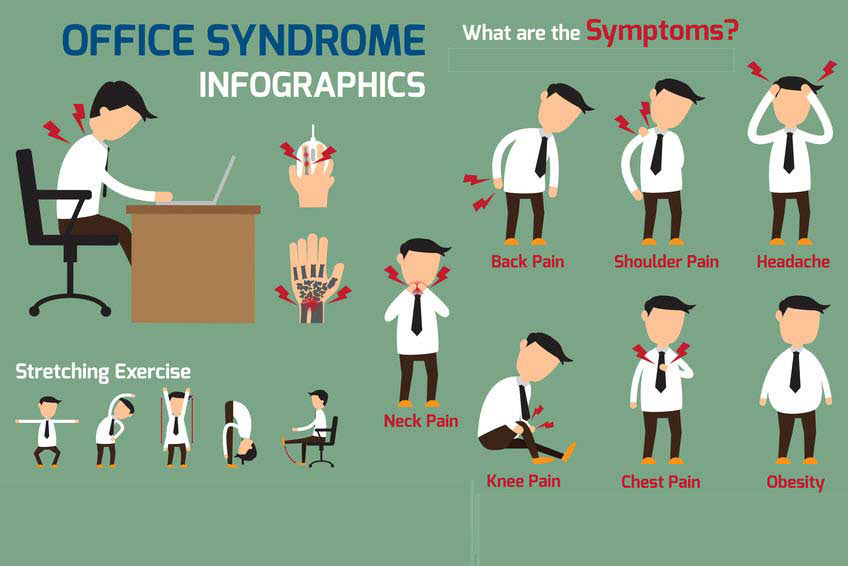
Whilst using DSE (Display Screen Equipment) all users may be prone to developing adverse health effects. Many of these can be avoided when the user is aware of the risks and uses the equipment in the correct manor. Some of the possible effects include:
- Musculoskeletal disorders
- Temporary visual problems
- Fatigue & stress
- Photosensitivity epilepsy
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
Potential risk factors
- Prolonged static posture of the back, neck and head
- Awkward positioning of the hands
- High workloads combined with tight deadlines
- Poor positioning of the display screen equipment
- Poor lighting, including glare and reflections
Epilepsy
Facial dermatitis
Some DSE Users have reported facial skin complaints such as occasional itching or reddening of the skin on the face / neck. These complaints are relatively rare. Available evidence suggests they may be associated with environmental factors such as air conditioning or low relative humidity within the office environment.
Radiation and pregnancy
Anxiety about radiation emissions from DSE equipment and possible effects on pregnant women has been widespread. Substantial evidence that these concerns are unfounded. No special protective measures are needed to protect the health of people working in this type of environment.
Workstations
DSE workstations can include the following equipment:
- Screen or monitor
- Keyboard & mouse
- Desk & chair
- Other parts of the computer…
- processing unit
- tower
- scanner
- Desk accessories…
- telephone
- files
- document holders
- Immediate work environment…
- lighting
- glare
- noise
- Computer accessories…
- docking station
- printer
- remote disc drives
Workstations needs to be assessed against requirements dictated by the relevant local regulations. The equipment must not be a source of risk for operators or users.
Equipment
Display screen
- The on screen characters must be well defined, clearly formed with adequate spacing.
- Stable image – not flickering.
- Adjustable brightness and contrast.
- Adjustable tilt and swivel.
- Free from Glare and reflections.
- Any problems should be reported to your Manager/Supervisor.

Keyboard
- The keyboard must be able to tilt and separate from the screen.
- Sufficient space in front of the keyboard.
- Matt surface.
- Arrangement of the keyboard must be suitable for the specific task.
- Symbols contrasted and legible.

Work desk
- Suitable for work activities.
- Low reflective surface.
- Allows flexible arrangement of the screen, keyboard, documents and related equipment.
- Document holder, stable and adjustable, positioned to minimise the need for uncomfortable head and eye movements.
- Adequate space for users to find a comfortable position.

Work chair
- Stable and allows the user easy freedom of movement and a comfortable position.
- The seat shall be adjustable in height.
- The seat back shall be adjustable in both height and tilt.
- A footrest shall be made available to any user who wishes to have one.

Peripheral devices
Peripheral devices such as mice and keyboards may also need to be user specific. The repetitive nature of mouse use, and the poor posture that is often adopted, leads to users experiencing discomfort in the wrist. There is currently no consensus for a suitable mouse shape. However, users who experience discomfort using one type of mouse may benefit from trying different designs.

Workstation setup

Head and neck
- The very top of the screen should be level with your line of sight.
- The screen should be directly in front of you.
- It should be at arm’s length distance away when you are sitting in an upright position.
Getting comfortable
- Ensure your feet are flat on the floor, with your knees at a minimum angle of 90 degrees.
- If you cannot place both feet on the floor whilst sitting right back in your chair, you need a footrest.
- Adjust your chair to support your back.
Arms
Ensure your elbows are level with the keyboard when sitting at your desk. This will position your wrists at the correct angle.
Over reaching
Items in frequent use, such as a telephone, stapler, pens etc. should be placed with easy reach.
Reviewing documentation
Keying in
Fine tuning
DSE poster
Download our ‘DSE Poster’ and display this poster insight of all DSE users to refresh their knowledge.
Work space requirements
The work station should be designed to provide sufficient space for the operator/user to change position and vary movement.
Space
Ensure the user is allocated a suitable workspace to ensure they can position themselves comfortably in front of their display screen.
Lighting
- Ensure there is satisfactory lighting conditions.
- Ensure there is appropriate contrast between the screen and background environment.
- Take into account the type of work, and vision requirements of the user/operator.
- Ensure there is no glare and reflections on the screen, this can be prevented by coordinating the workstation layout with the positioning of the artificial light sources.
Noise
Noise levels in the area should be reduced to the lowest level possible to prevent distraction from the work being carried out.
Heat
Equipment belonging to any workstation must not produce excess heat which could cause discomfort to operators/users.
Radiation
Any radiation likely to be generated by DSE is well below the limits set by the National Radiological Protection Board as posing a risk to health. If employees are concerned, they should be reassured that the radiation emitted by DSE is not likely to harm them.
Humidity
Humidity must be maintained at adequate levels. A dry atmosphere may cause dry and itchy eyes. A moist atmosphere may make the user clammy and uncomfortable.
DSE users
DSE users are workers who use DSE daily, for continuous periods of an hour or more, for whom we have to make additional considerations..
Additional considerations
Software
All software must be designed to allow the user to interact with the programs without increasing the stress or strain. Some users, especially those with Dyslexia may benefit from Assistive Technology e.g. screen colour changing or voice to text dictation software.
Daily work of DSE users
- The timing of the break is more important than the length. Taking a break before the onset of fatigue will prevent discomfort and reductions in productivity.
- Rest breaks must be incorporated into work time and must not result in a greater intensity of work.
- Short, frequent breaks are preferable to occasional, longer breaks; five minutes every hour will help to prevent fatigue and will benefit the user.
- Rest breaks should be taken away from the screen whenever possible. This helps to rest the eyes and encourages change in posture.
- Visual fatigue can be eased by frequently changing the eye’s focal distance, particularly looking away from the screen.
- Wherever possible, users should choose how they carry out tasks to enable them to distribute their work, incorporating changes of activity and rest breaks.
Eye care


