Introduction
The aim of this toolbox talk is to increase staff awareness of the point of entry that hazardous substances can take in order to cause injury.
The use of regular toolbox talks, if done effectively, will significantly improve the safety culture within your organisation. This will increase the safety awareness of the workers, and as a result reduce the likelihood of accidents and unsafe occurrences.
Legislation references
- Health & Safety at Work Act 1974
- Control of Substances Hazardous to Health 2002 (COSHH)
Hazardous substances awareness
There are 4 routes for hazardous substances to enter the body:
- Absorption
- Ingestion
- Inhalation
- Injection
Absorption
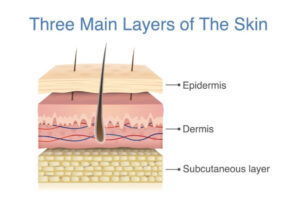
- Agents pass into and across the skin tissues
- Damage may occur locally or agent may be carried to other areas of the body
- Examples include pesticides or weed killer
Ingestion

- Substances taken into the body through the digestive tract
- Effects may be local or may occur in other areas of the body
- May be direct (i.e. eating a poison) or indirect (i.e. from dirty hands)
Inhalation

- Substances can be taken into the body through the breathing process
- May have local effects or be carried to other areas of the body
- Examples include dusts fumes gases vapors mists aerosols
Injection
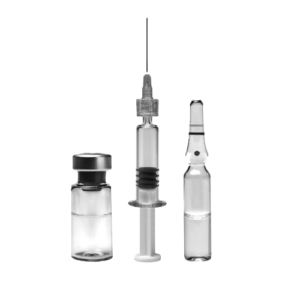
- Agent is injected into the body through the skin
- May act locally or be transported to other organs and tissues
- Typically from sharps (i.e. used needles or charged hypodermic syringes)
- Agents in pressurised systems can be injected through hoses or failure points.
- There need not be damage to the skin.

